Introductory Guide
Elaine Chung
Learn about the various elements involved in learning the piano with our comprehensive guide. As an experienced piano teacher, we cover key areas such as ear training, sight-reading, physiology, technique, expression, and repertoire. Whether you’re a beginner or an intermediate pianist, our guide offers tips and techniques to help you achieve your musical goals. Join us on this musical journey to grow your passion for music and become a skilled pianist.
Key Distribution
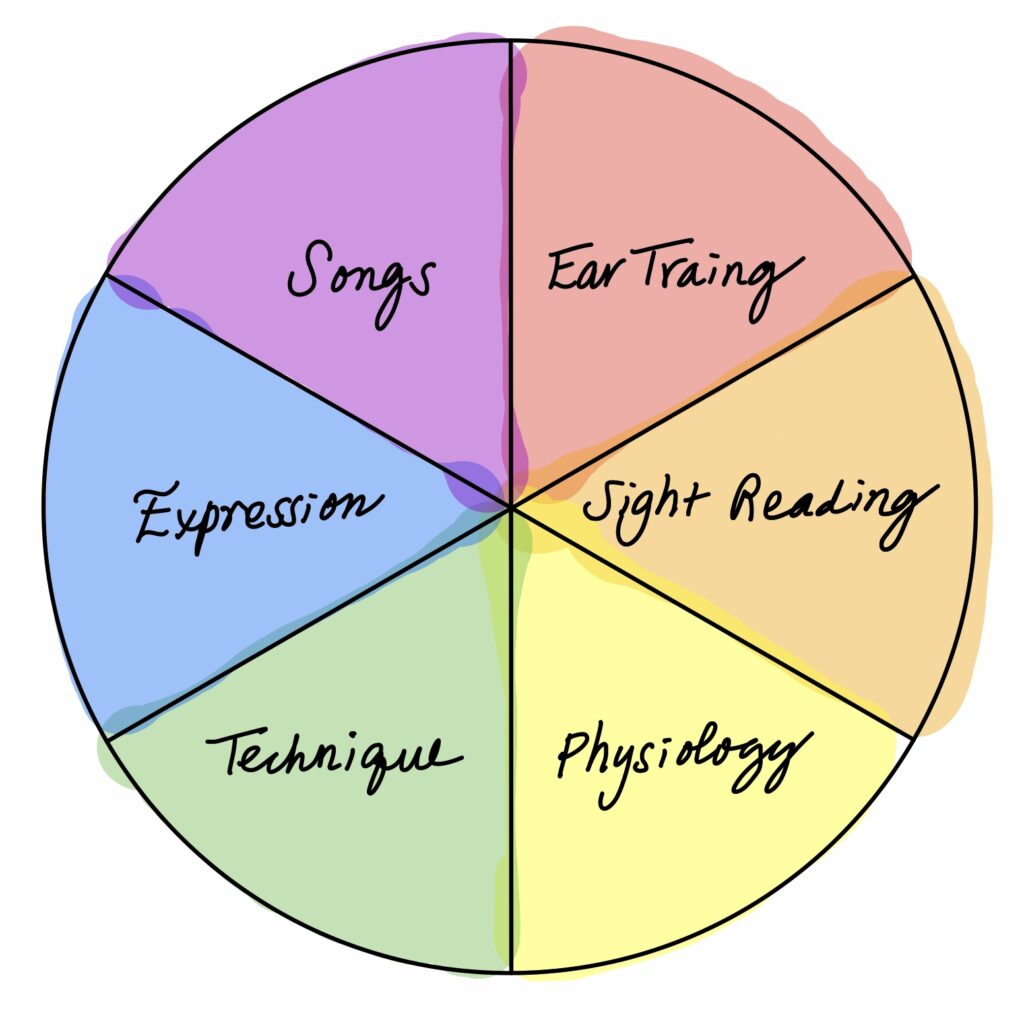
Playing the piano is a multifaceted activity that involves more than just pressing keys and reading notes or playing at high speeds. Based on my teaching experience, I have identified the key areas involved in learning music, and this guide provides a comprehensive overview of each of these areas.
EAR TRAINING: Young children can develop a valuable aural skill through appropriate stimulation, which can aid in their journey towards becoming a musician. Caregivers can help raise audiation skills by singing or chanting with their children in a positive setting, while ear training apps can also be beneficial. Although Edwin Gordon suggests that nine years is the maximum age for growth in aural skills, my experience as a teacher has shown that younger students may already have reached their maximum capacity for such skills due to their brain development. As children age, the progress rate for developing aural skills is likely to decrease.
SIGHT READING: After gaining proficiency in literacy and math, note-reading training can begin using a variety of techniques such as apps and traditional methods to enhance sight-reading skills. However, I observed a gap in current methodologies, leading me to create a unique note-reading system through extensive research and development. The public will have access to this system in winter 2023.
PHYSIOLOGY: Physical strength and relaxation techniques are crucial to playing the piano, as it involves the use of fingers. Studying physiology can help students understand how movement affects the effect of emotions. (further reading: Physical Basis of Music, E. T. Jaynes, The Physiological Mechanics of Piano Technique, Otto Ortmann)
TECHNIQUE: In piano playing, technique involves developing finger dexterity, independence, and control of body movements. To prevent injuries caused by unwanted tension, a proper understanding of physiology is necessary, and practicing advanced techniques without this knowledge can be dangerous. Tendonitis is a common injury among pianists who practice for prolonged periods without taking breaks. Junior and intermediate level students work on various exercises to build their basic techniques.
EXPRESSION: Expressive qualities are essential to a piano performance, and we must gain skills in physiology and technique concurrently to discuss and apply expression effectively. Parents can help children develop such sensitivity through discussions using personification, metaphors, imagination, making stories, singing, dancing, drawing, painting using colors, and sharing thoughts and feelings while listening to songs.
REPERTOIRE: Building a wide range of repertoires from different stylistic periods can broaden your perspective and help students grow a passion for music. Attending concerts, masterclasses, and festivals and bonding with friends who love music can help increase the exposure of new songs.
The proportion of the above categories may adjust to match your goal, depending on the group division you have selected. A decent piano is recommended, preferably an acoustic one, but a digital piano may be suitable for group 1 beginners. A metronome comes in handy, and a pedal extender is required for groups 2 and 3 students if their heels cannot reach the floor when using the pedal in a sitting position. A step stool will correct postures for all young students.
In conclusion, learning the piano is a journey that involves various elements that work together in harmony. It is not only about reading notes and pressing keys but also about developing aural skills, note-reading abilities, physical strength, and relaxation techniques, and expressive qualities. Through the guide presented in this article, we hope to provide a clear idea of what it takes to learn the piano in every part of the journey. We encourage parents and students to explore the various resources and tools available to aid them in their learning process. With consistent practice, dedication, and passion, anyone can become a skilled pianist and enjoy the beautiful world of music.
NEXT> ADVANCED CURRICULUM

